As the number of ESCO implementers increases, the range of uses of the classification is widening. The European Commission aims to illustrate how ESCO concepts can be connected and used. With the new ESCO Skill-Occupation Matrix Tables, the Commission is showcasing potential interrelations based on the ESCO skills and occupations structures.
The ESCO Skill-Occupation Matrix Tables are now available to connect ISCO-08 occupation groups (rather than one single occupation) to ESCO skills hierarchical groups (rather than one single skill).
Starting from the most granular level of the ESCO classification, the tables show the share of ESCO skills within ISCO-08 occupation groups.

With these tables, ESCO implementers are free to choose different ESCO crosswalks between the occupation and skills pillar at various levels of granularity, depending on their use case.
Methodology
The Skill-Occupation Matrix Tables have been developed using data available in the Download Section of the ESCO portal, and the methodology employed is available in the Technical Report posted below. Implementers can choose which level of the ISCO hierarchy for occupations (levels 1, 2, 3, 4) and which level of the ESCO hierarchy for skills (levels 1, 2, 3) to adopt. The tables can be downloaded below and in the Publication section of the ESCO Portal. If needed, the ESCO team is available to provide further support and share XLS tables of the requested size (e.g. a table showing matches between ISCO level 2 and ESCO level 3).
Visualisation
The resulting heatmap below shows in a more user-friendly way the relationship between the first level of ISCO occupation groups and ESCO skills groups. When reading the table, users should look at occupations (rows) and then compare the distribution of skills between different occupation groups. For example, looking at Plant and machine operators and assemblers, one observes that workers in this group have a higher share of Working with machinery and specialised equipment skills (27%) compared to Management skills (5%). Skill groups (columns) are not to be compared.
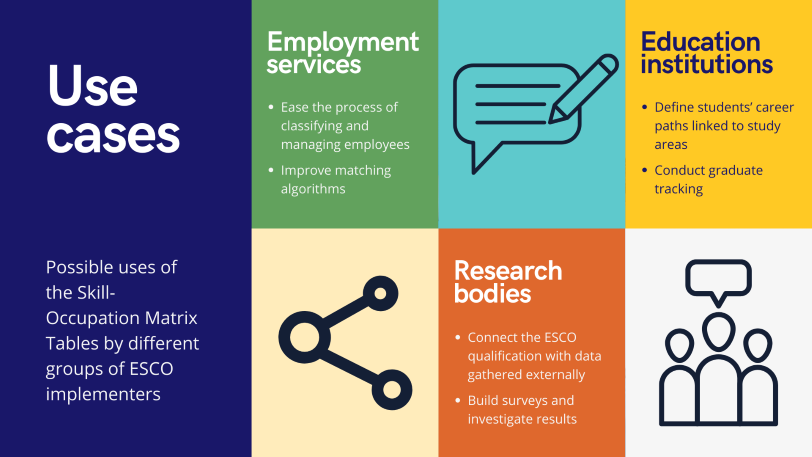
Use cases
These Skill-Occupation Matrix Tables can support ESCO implementers and other stakeholders to improve their services and ease their implementation of ESCO. Some use cases are briefly summarised in the infographic below. More information is available in our Technical Report.
Learn more
Skills-Occupations Matrix Tables and Report
Here you can download the Matrix Tables (excel file) and the Technical Report.
